
Payload Ethernet type (five choices are supported: IPv4, IPv6, PPPoE-all, PPoE-discovery, and PPPoE-session).Outer 802.1p CoS bits, inner 802.1p CoS bits, or both.Both QinQ (inner and outer) VLAN tags, or both 802.1ad S-VLAN and C-VLAN tags.Single 802.1Q VLAN tag, priority-tagged, or 802.1ad VLAN tag.Service instance is associated with a bridge domain based on the configuration.Īn incoming frame can be classified as service instance based on the following criteria: Of an EVC on a given port on a given router. In the Cisco EVC Framework, theīridge domains are made up of one or more Layer 2 interfaces known as service instances. It embodies the different parameters on which the service is being offered. Displaying and Verifying Bridge Domain Interface ConfigurationĪn Ethernet Virtual Circuit (EVC) is an end-to-end representation of a single instance of a Layer 2 service that is offeredīy a provider.
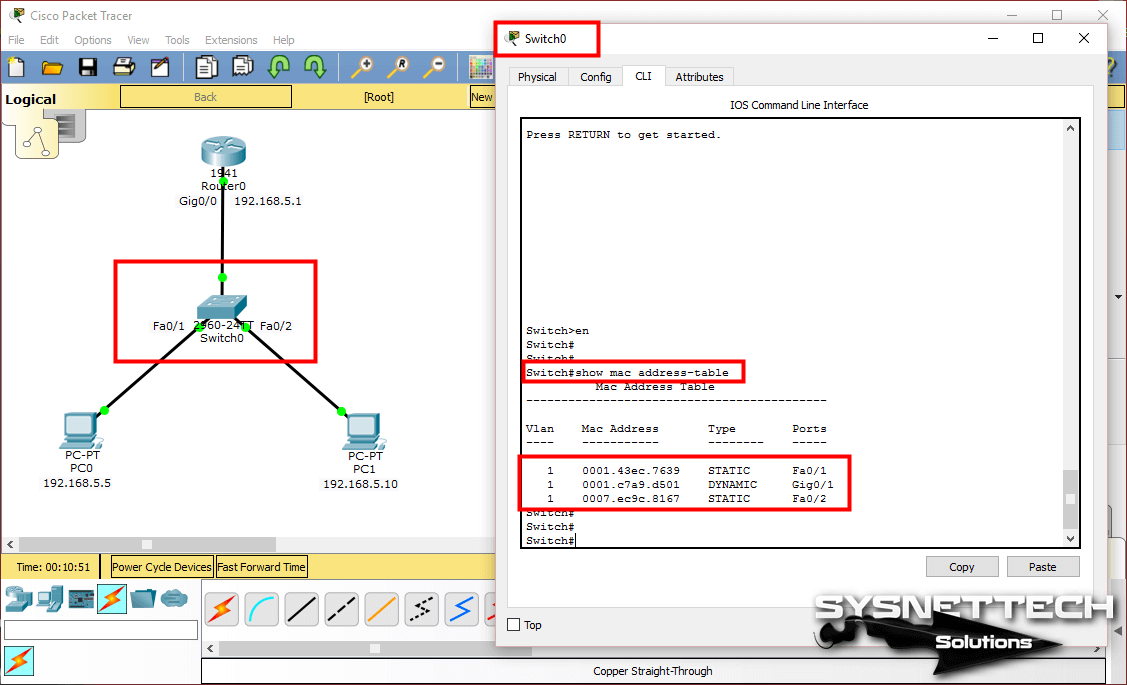
#SHOW MAC ADDRESS OF CISCO ROUTER INTERFACES HOW TO#
How to Configure a Bridge Domain Interface.
Creating or Deleting a Bridge Domain Interface.Link States of a Bridge Domain and a Bridge Domain Interface.Prior to configuring a bridge domain interface, you must understand the following concepts: Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), G-ARP, and P-ARP handling.
Only one bridge domain interface can be associated with a bridge domain.īridge domain interface supports the following features: Eachīridge domain represents a Layer 2 broadcast domain. Bridge domain interfaces are identified by the same index as the bridge domain. Bridge domain interface is a logical interface that allows bidirectional flow of traffic between a Layer 2 bridged networkĪnd a Layer 3 routed network traffic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
